The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), based in Meyrin, a suburb of Geneva, is one of the world’s largest centers for scientific research. Established in 1954, CERN was founded with the mission to explore the fundamental questions of physics, particularly the nature of matter and the forces that govern the universe and to promote scientific collaboration around the world. CERN comprises 24 member states and hosts thousands of scientists from over 70 countries, making it a symbol of international scientific cooperation and innovation. In addition its groundbreaking research in physics, CERN is also a hub of technological innovation. It played a crucial role in the development of the World Wide Web, which was invented at CERN in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee to meet the demand for information sharing among physicists.
LHC
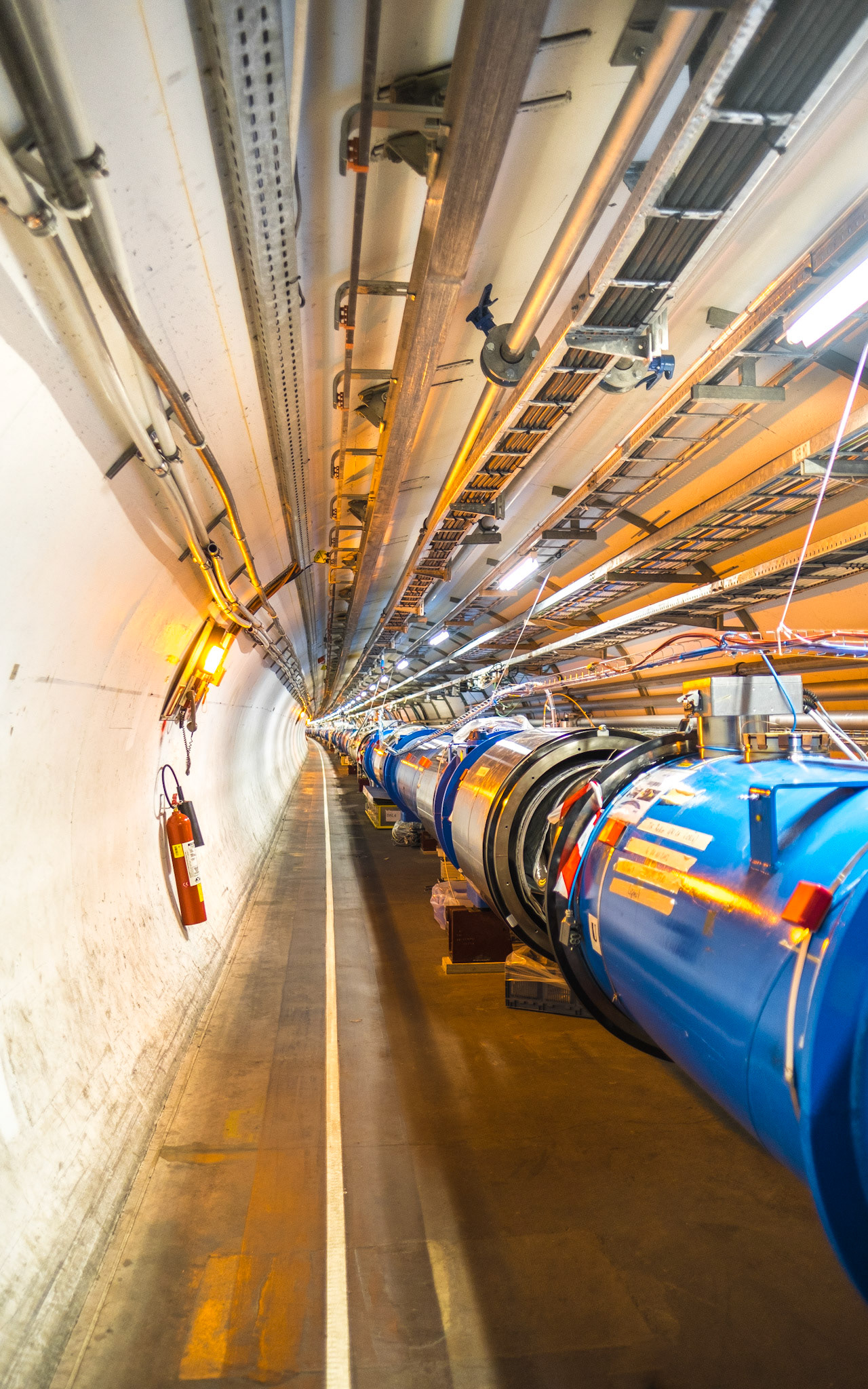
CERN is home to the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator, located in a 27 kilometer long circular tunnel beneath the French-Swiss border. The LHC can accelerate protons to a speed only about 11km/h slower than the speed of light, which means that they do more than 11000 revolutions per second in the ring ! It is used to collide particles at extremely high energies to simulate conditions similar to those just after the Big Bang. One of the most significant discoveries made at CERN was the Higgs boson in 2012.
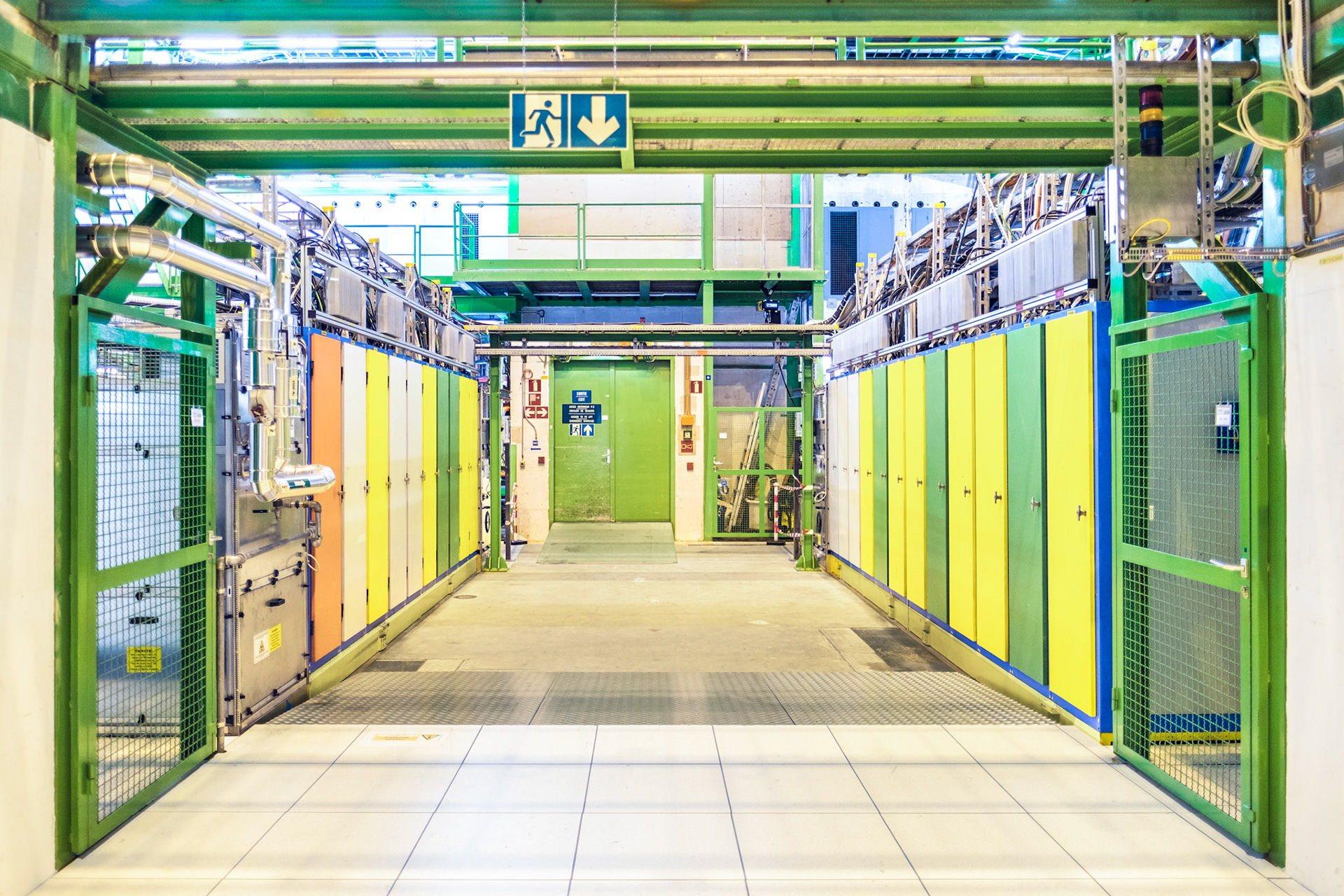

equipment 140m below the surface
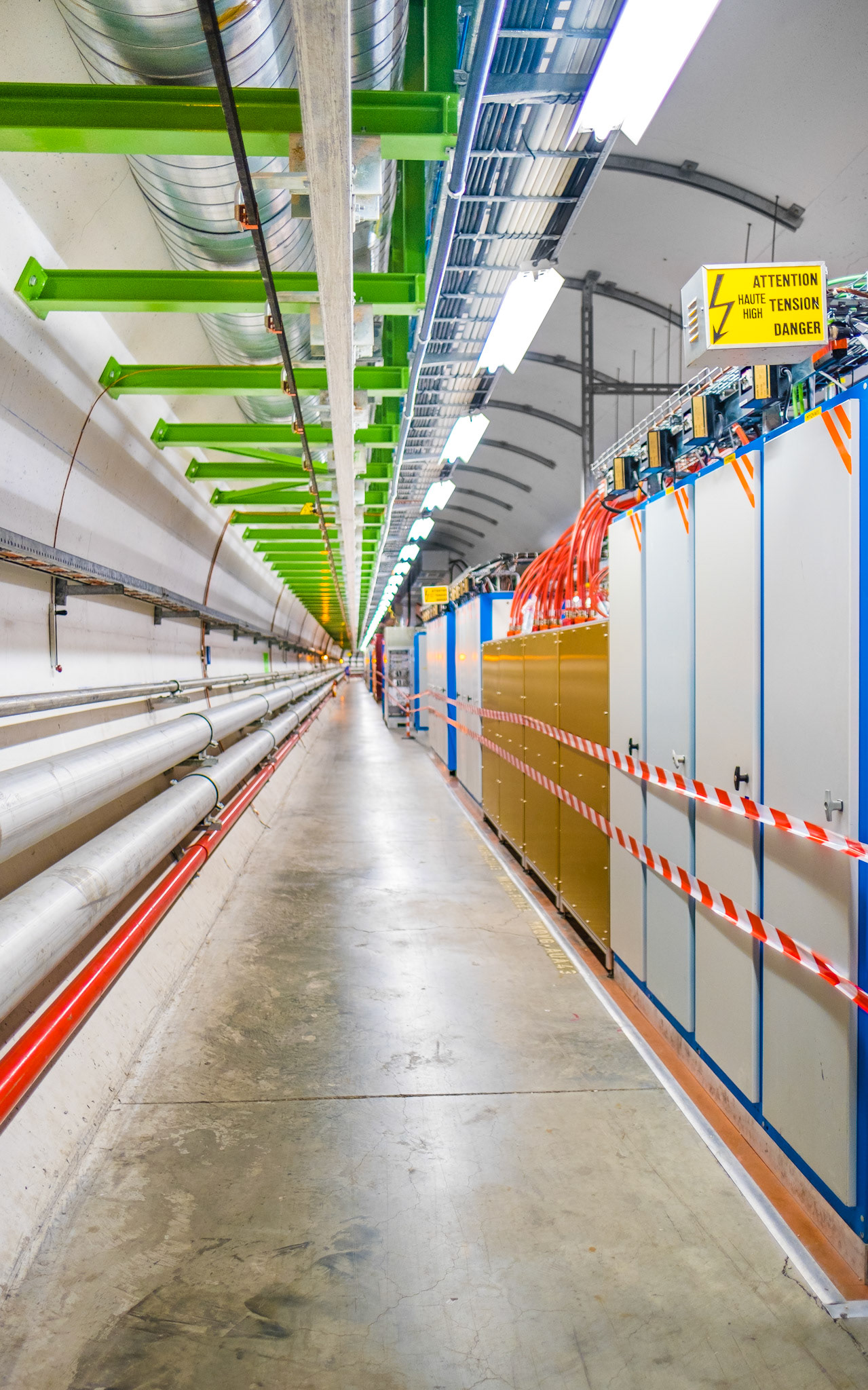

access tunnel to the LHC
The tunnel used by the LHC is located at a depth ranging from 50 to 175 meters below the surface and was constructed between 1983 and 1988.
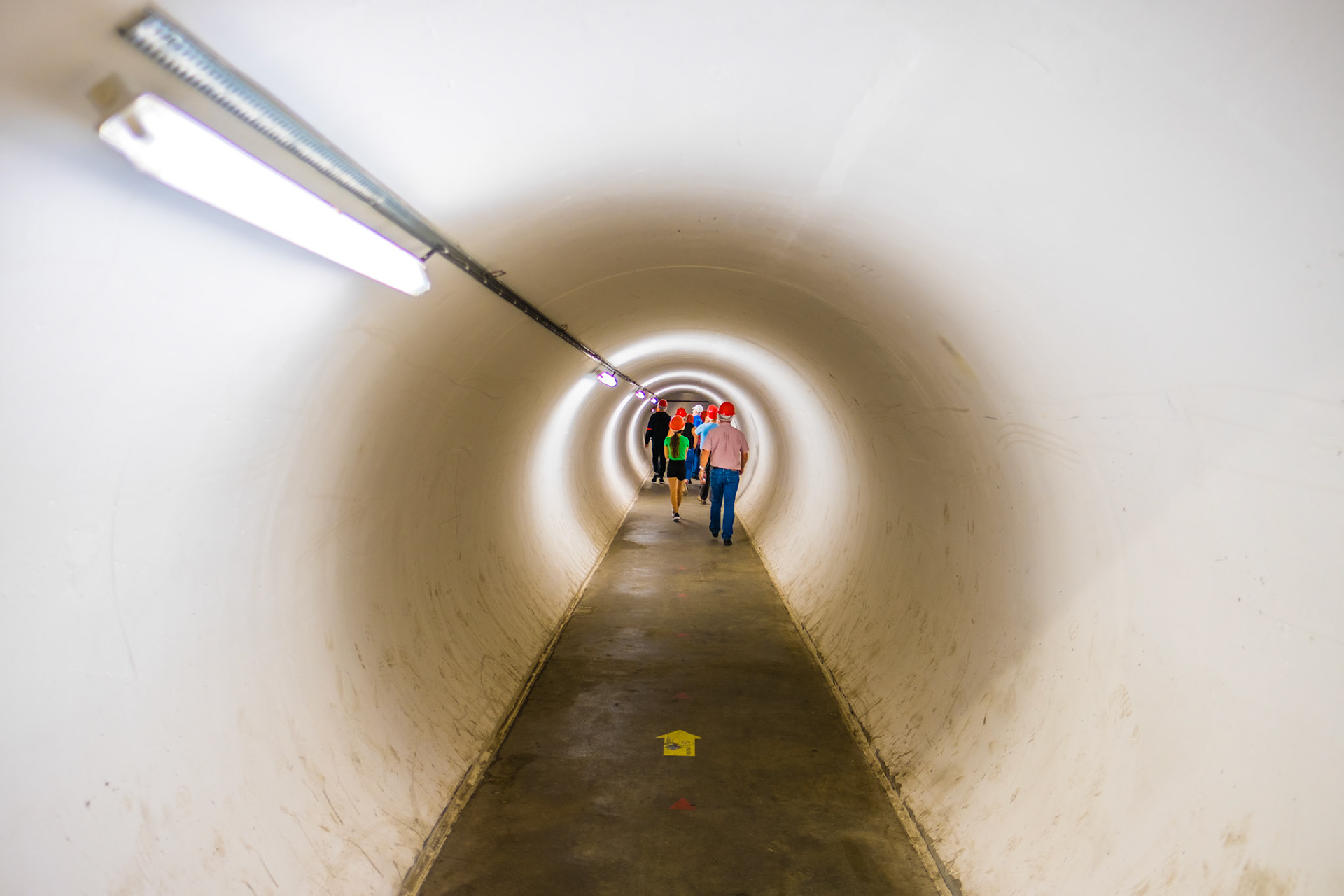

access tunnel to the LHC
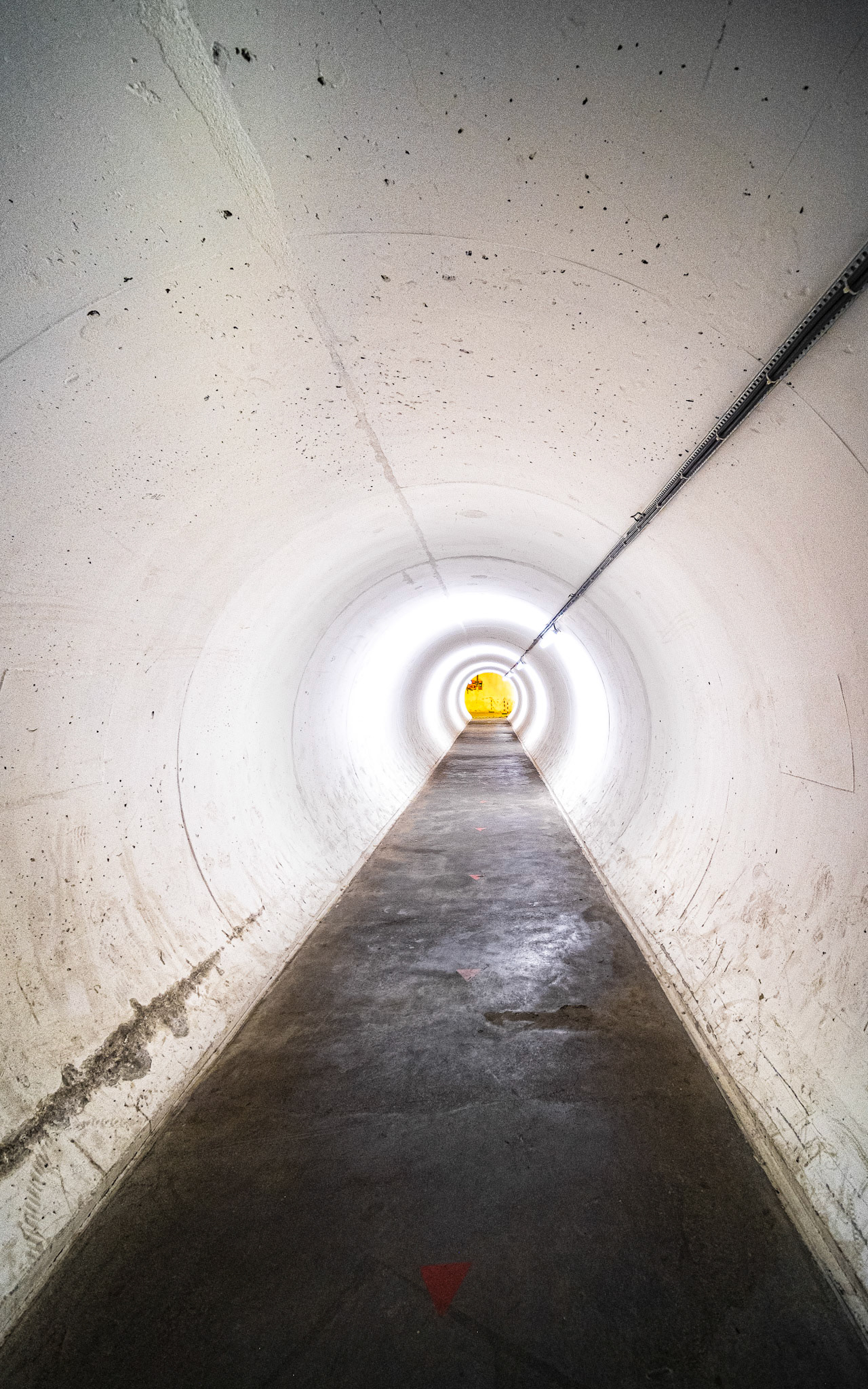

access tunnel to the LHC
The collider tunnel houses two parallel beamlines, each containing a particle beam moving in opposite directions around the ring. At four specific points along the tunnel, these beams cross paths, creating the locations where particle collisions occur.

LHC
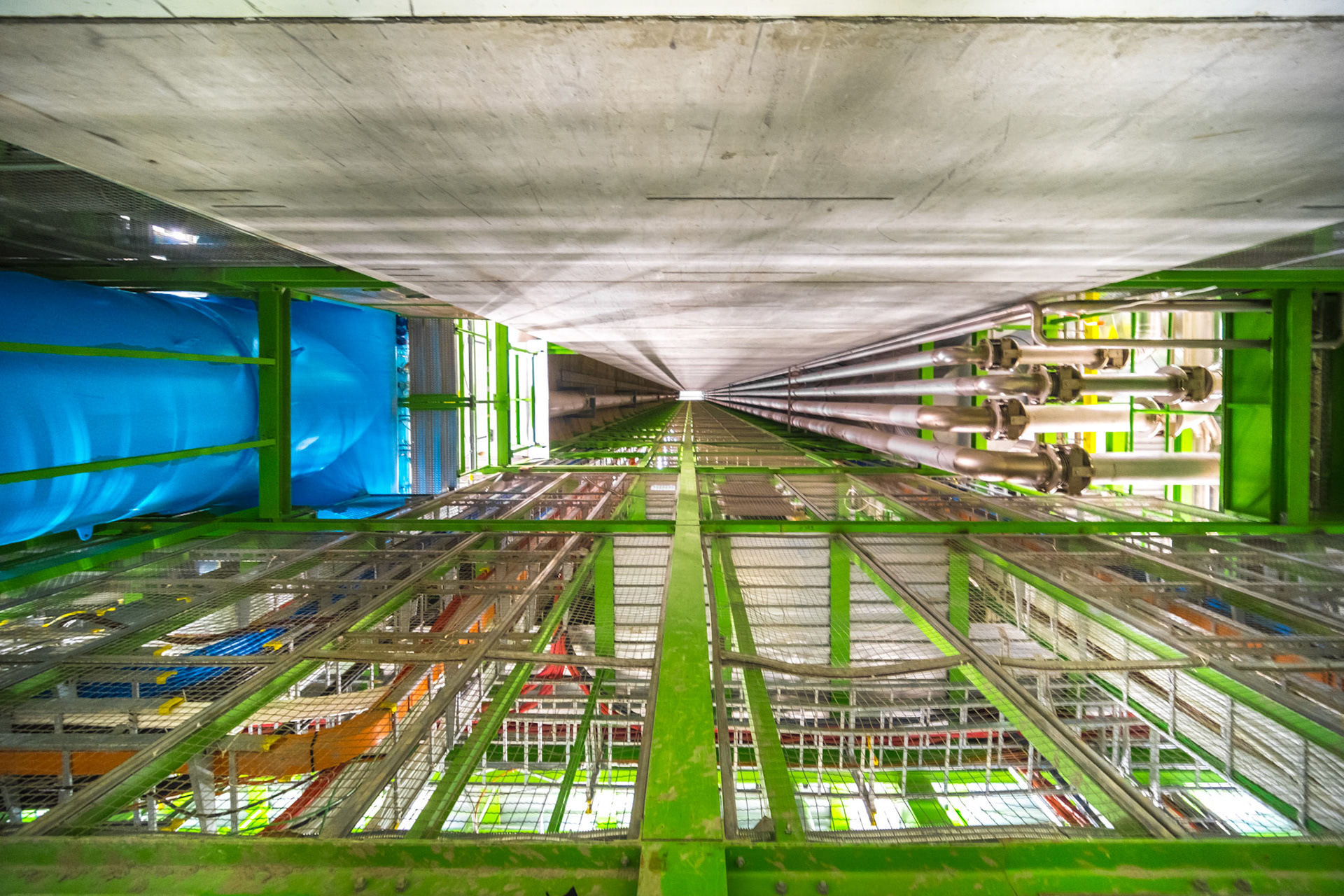

Looking up
Nine detectors have been constructed at the intersection points of the LHC. Two of these, the ATLAS and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS), serve as large general-purpose particle detectors.
CMS
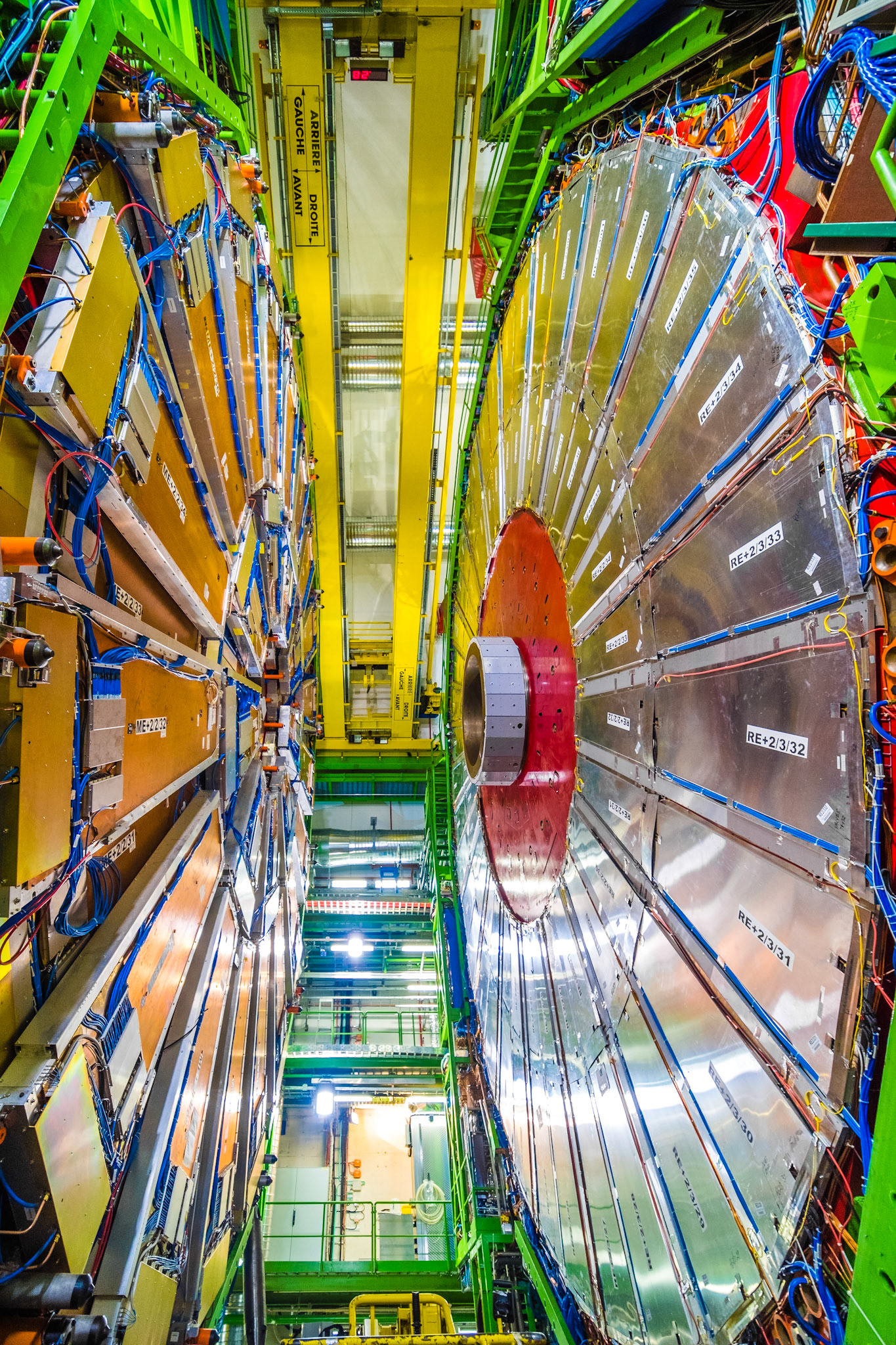
The complete CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid) detector is 21m long, 15m wide and high and has a weight of 14,000 tons ! Located 100 meters below the surface at Cessy in France, it’s famous for being part of the Higgs boson discovery.
The following photos show one slice of the CMS detector.
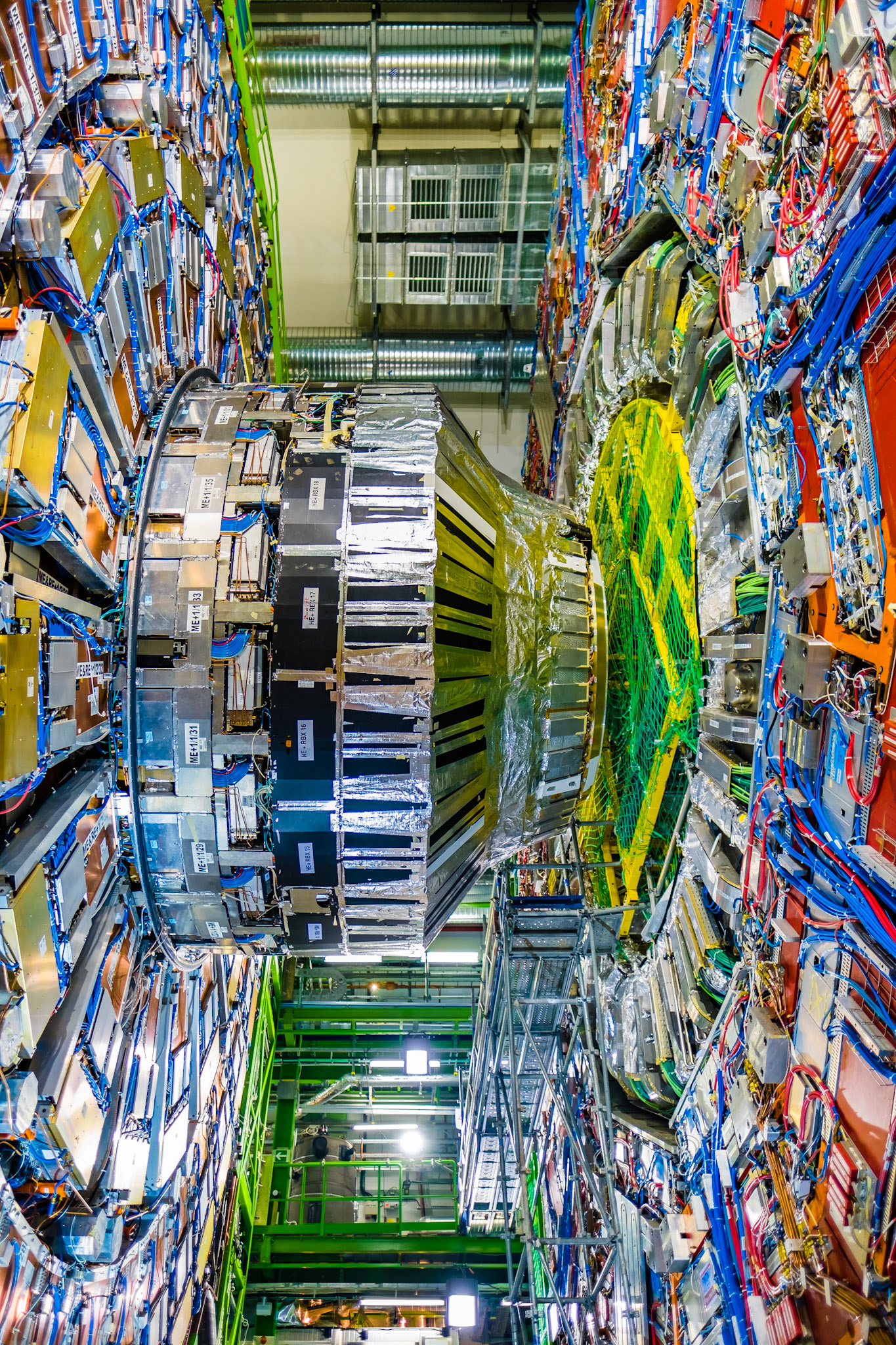

CERN CMS
CERN CMS
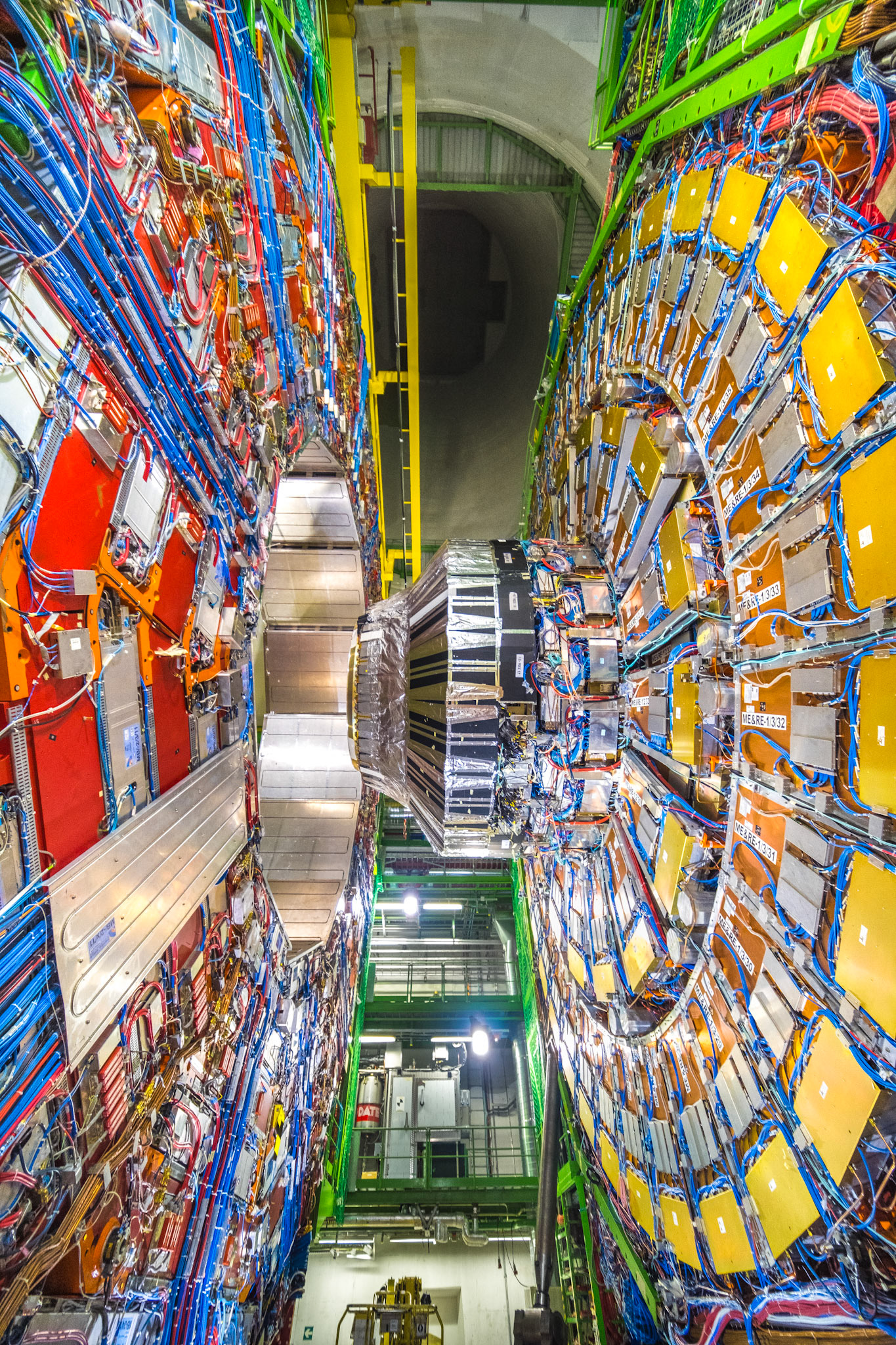

CERN CMS
All photos were taken during the CERN Open Days in September 2019.
You may also like